Lithium is a promising anode candidate for future high-energy-density batteries thanks to its light weight and the fact that it has the highest theoretical capacity (of 3860 mAh/g) and the lowest electrochemical potential of all metals. However, it does suffer from several serious problems, one of which is that its volume drastically changes during battery recycling. Now, a team of researchers from Stanford University in the US has tackled this problem head-on by confining lithium anodes inside the interlayer gaps of "lithophilic" layered reduced graphene oxide. The new composite anode keeps up to around 3390 mAh/g of its capacitance, has a low overpotential of roughly 80 mV at 3 mA/cm2 and other good properties, such as a flat voltage profile in a carbonate electrolyte.
"By designing a layered lithium-reduced graphene oxide structure, we have solved the "infinite relative volume change" problem that plagues lithium metal," explains team leader Yi Cui. "This problem has long been ignored in research on lithium anodes, but it is an important one since most of the difficulties encountered with lithium metal – such as unwanted dendrite growth and unstable solid electrolyte interphases – stem from this."
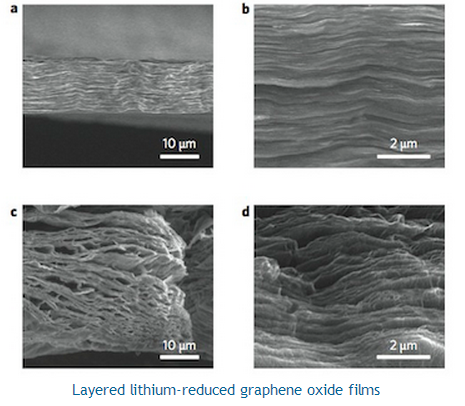
The researchers began by using a technique called vacuum filtration to prepare graphene oxide film from well-dispersed graphene oxide solution. Next, they contacted the film with molten lithium. The "spark reaction" that occurs between the two materials not only instantly reduces the graphene oxide but also opens up uniform nanoscale interlayer gaps within the carbon-based sheet. These gaps can then be used to host the lithium metal.
Graphene oxide surface becomes "lithophilic"
"Following this reaction, we found that the surface of graphene oxide becomes "lithophilic"," says Cui. "Lithophilic is a word we made up by combining "lithium" and "-philic" to explain that molten lithium "likes" the graphene oxide surface a lot and wets it quite well."
Cui says that his team also found that the capillary force of the nanoscale gaps is so powerful that it can infuse molten lithium into the gaps. "After cooling down the film, we get a lithium-reduced graphene oxide electrode that has a well-established layer-by-layer stacking architecture."
According to Cui and colleagues, the new composite anode could be used in high-energy-density and high-power lithium batteries.
The researchers say they are now busy further improving the electrode so that it does not change in volume at all during cycling. "Ultimately, we hope to solve the other problems that lithium metal suffers from and hopefully develop a large-scale fabrication technique to fabricate this composite material at low cost," says Cui.

